What is design thinking?
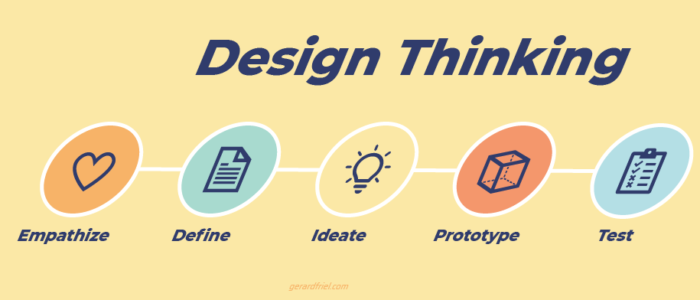
Design thinking is a user-centric approach to design. It combines a mindset, principles, tools, and activities to help you solve design problems in a creative way. A common design thinking model consists of five key stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
What are the benefits of using Design Thinking?
Popular in the product design and UX/UI world, design thinking is also being used in other areas such as learning design as it:
- Places the learner’s needs into focus – taking a human-centric approach
- Questions assumptions
- Leads to greater creativity and innovation by considering more ideas
- Tests ideas with learners to get insightful feedback
- Saves development time and money
The 5 Steps of Design Thinking
Empathize
Purpose – Get to know your learners so you can understand and anticipate their needs. This is a learner-centric approach that provides insights to help you accurately define the problems that need to be solved.
Tools – Shadowing, interview, survey, empathy map, user journey map, persona.
Define
Purpose – Use the insights gathered during the empathize stage to define the problem. This will then provide direction when solutions are being considered during the ideate stage.
Tools – Problem statement (pain points and frustrations), hypothesis statement (a best guess on how to address the problem), and value proposition (features and benefits).
Ideate
Purpose – This is where the creative and innovative magic happens! The purpose of the ideation stage is to generate as many ideas as possible whilst reserving judgement. Best results are from a mix of people across various roles (such as design, tech, users, and stakeholders) with collective voting on which ideas to progress to prototype.
Tools – Goal statements, ‘how might we’ problem reframing, brainstorming, SCAMPER, Crazy 8s.
Prototype
Purpose – Develop the most promising ideas into something that can be tested by users. By creating a minimum viable product (MVP), you can save time and money by testing low-fidelity prototypes where changes can be made quickly.
Tools – Paper sketching, storyboarding, low-fi interactive prototype.
Test
Purpose – By getting early prototypes to your learners, you can get early feedback and useful insight. This enables you to iterate on your ideas and prototypes to solve your learner problems.
Tools – Real-time testing, survey, interview, review.
Using Design Thinking – A non-linear approach
The design thinking model resembles a linear model going from the empathize to test phase. However, it is used effectively in a non-linear way and you can return to a previous step of the process.
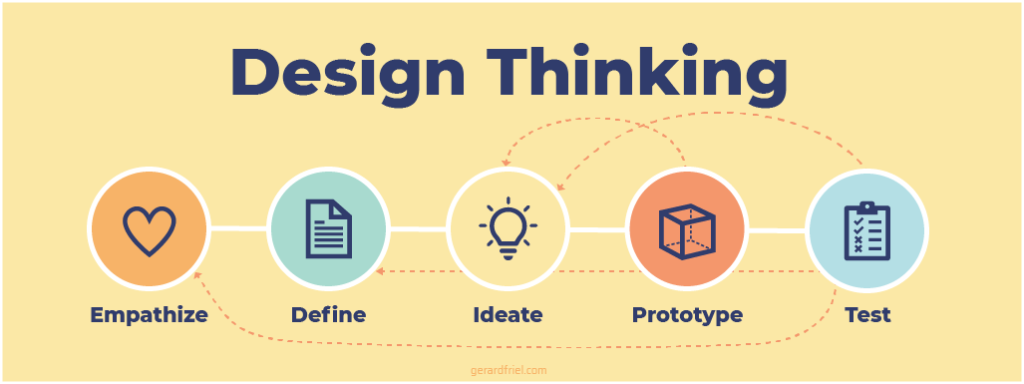
A common loop taken is the iteration loop at the end of a test, where learner feedback is gathered and the information is used to improve the prototype. This leads to further ideation activities and prototype development.
Review

Pros: Creative thinking, learner-centric, tests your assumptions, cross-functional team collaboration.
Cons: While well suited to product-based development, for instructional design projects there are additional elements to consider that are not part of the model such as project initiation and implementation.
Related reading: ADDIE, SAM, Instructional Design
